The greenhouse effect of Venus From geometry, we can calculate the average solar flux over the surface of Venus It is approximately 661 W/m2 Venus is very reflective of solar radiation In fact, it has a reflectivity (or albedo) of 08, so the planet absorbs approximately 661 X 02 = 132 W/m2 By assuming that the incoming radiation equals the The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effectThe panel refers to warming due to increased atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases as "greenhouse warming" Measurements of atmospheric CO 2 show that the 1990 concentration of 353 parts per million by volume (ppmv) is about onequarter larger than the concentration before the Industrial Revolution (prior
Draw A Well Labelled Diagram To Explain The Greenhouse Knowledgeboat
Global warming greenhouse effect diagram drawing
Global warming greenhouse effect diagram drawing-Modern global warming is the result of an increase in magnitude of the socalled greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and other greenhouse gases In 14 the IPCC reported that concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrousThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change
This project based instruction unit focuses on the issues, causes, effects, and prevention of global warming The project is designed to be taught to an Algebra I class, implementing the mathematical reasoning behind global warmingCopy Table 81 below that shows the global warming potential and the persistence of each of these gases Be sureEnergy resources diagram "Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of
Guest post by Kevin Judd Climate scientists are telling us that gases like carbon dioxide are causing global warming Carbon dioxide is produced when petrol is burned in your car engine, or when coal and gas are burned at powerstations to make electricity Carbon dioxide causes global warming because it contributes to the socalled greenhouse effectGreenhouse Effect On Earth, Greenhouse Gases Absorb Infrared Radiation Emitted From Earth And Reradiate It Back, Thus Contributing To The Greenhouse global warming related process infographic template process timeline chart workflow layout with linear icons ecosystem diagram stock illustrationsWhat changes does it undergo while on Earth?
250 greenhouse effect diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect diagram stock video clips of 3 global warming, sun earth diagram energy global problems effects global warming greenhouse effect global waste management greenhouse effect vector global warming icons greenhouse gas effectThe greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientific process 4 Hypothesize about the effects of global warming on the climate and the world's populations 5 Conduct research using a variety of primary sources to explore perspectives in the global warmingWhat – specifically – does the term "global warming" refer to?



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Example Of Student Drawing Based On Textbook Diagram Download Scientific Diagram
Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factorsThe Greenhouse Effect Task Easy Draw a labeled diagram to model your teacher's description of the greenhouse effect Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere and warms the Earth's surface The heat is radiated back towards space Most of the outgoing heat is absorbed/trapped by greenhouse gas molecules in the Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse Effect Global warming describes the current rise in the average temperature of Earth's air and oceans Global warming is often described as the most recent example of climate change Grades 11, 12 Subjects Earth Science, Meteorology, Geography Contents 6 Images



Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Anthropogen Global Warming Png 750x525px Greenhouse Effect Area Atmosphere Of




Graphic The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
Have students create a diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect using paper, markers, etc Tell them that they will be asked to go home and explain the Greenhouse Effect and global warming to a family member using their diagram as part of a homework assignment Have them practice presenting global warming using their diagrams with peer partnersLevels, causing global temperature to rise over 1oF Think about it Draw a picture or diagram that shows the relationship between carbon dioxide, the carbon cycle, and the greenhouse effect Be sure to label and explain your drawing/diagram Figure 2 The Natural and Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Source EPAWith your group members, talk about the greenhouse effect on a global scale On a large white board, draw a diagram to represent your group's initial ideas about what is happening to the energy that enters the Earth's system when light from the Sun shines on the Earth Where does this energy go?




Greenhouse Effect Vs Global Warming Drawing Easy Drawing For Kids Youtube



Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That is a great way for students to combine images and text in a creative way to produce quick and clear scientific diagrams Students are going to recreate a model of the greenhouse effect using arrows to show how radiation movesGlobal Warming Experiment Background Information Our Climate is changing because humans have increased the amount of Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere Greenhouse Gases are actually necessary, as they help to keep the earth's surface warm by trapping the earth's heat (the greenhouse effect)Page 2 of 5 Describe, using a chart, how thermal energy is transferred within the atmosphere 10 Draw a diagram of the Coriolis effect Page 3 of 5 11 What are the four main greenhouse gases?




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Imagequiz Outline Drawing Tool
Climate Forcings and Global Warming Any changes to the Earth's climate system that affect how much energy enters or leaves the system alters Earth's radiative equilibrium and can force temperatures to rise or fall These destabilizing influences are called climate forcings Natural climate forcings include changes in the Sun's brightnessStudents explore climate change and global warming with multimedia They create a model of the greenhouse effect and then refine their findings using a demonstration and interactive Next, students research and diagram carbon sources and sinks Finally, they organize and analyze data to draw evidencebased conclusions regarding atmospheric carbon concentrations and localUse the back of this worksheet if necessary



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic
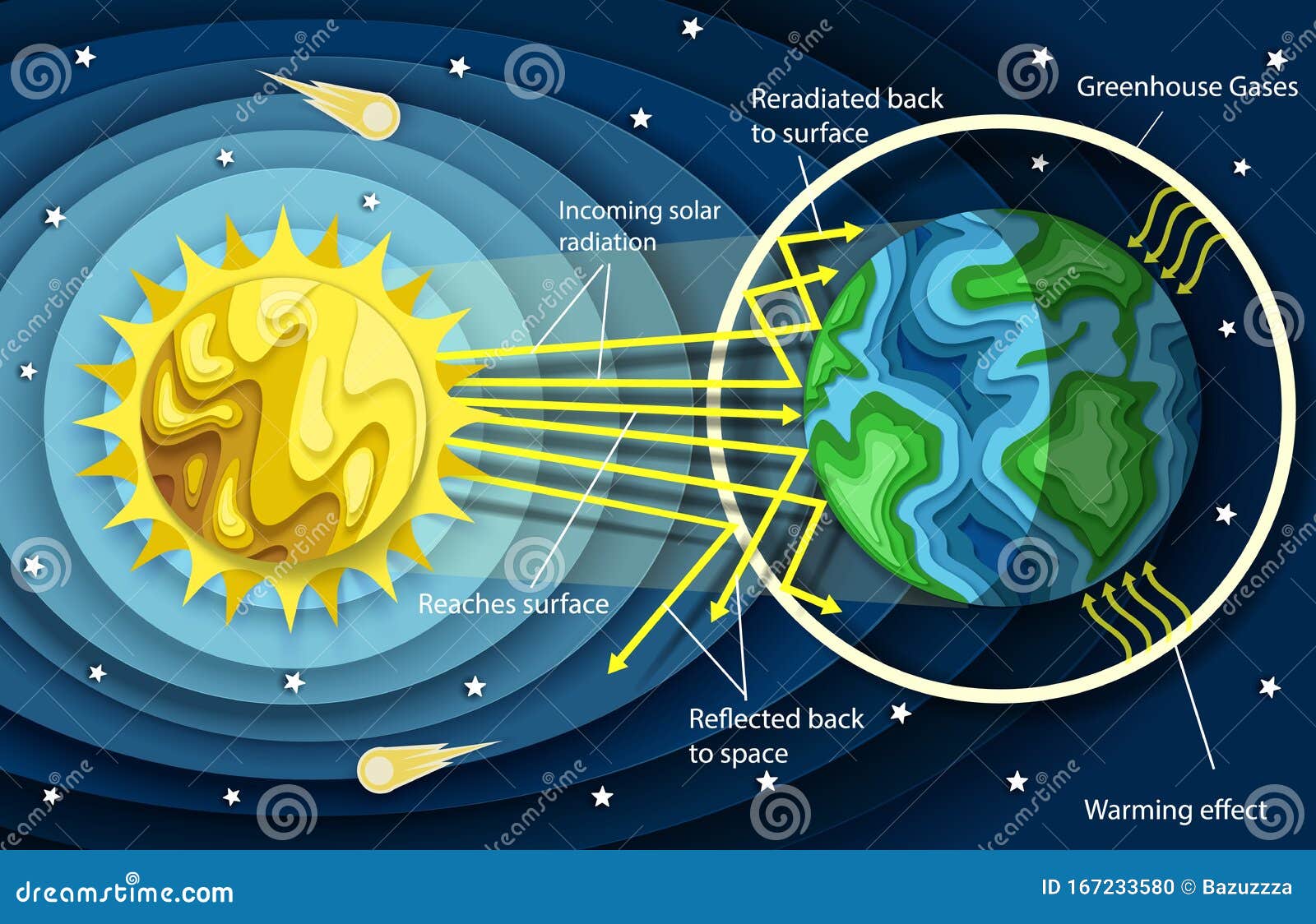



Vector Layered Paper Cut Style Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Ozone Greenhouse
Carbon dioxide controls the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere and thus the size of the greenhouse effect Rising carbon dioxide concentrations are already causing the planet to heat up At the same time that greenhouse gases have been increasing, average global temperatures have risen 08 degrees Celsius (14 degrees Fahrenheit) since 10 If the atmosphere works too well as a greenhouse, each day gets a little warmer and a little warmer We may not be able to measure this effect from day to day or even year to year But over tens of years, a few degrees of warming starts causing changes For example, ice melts in the North and South Pole regions Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
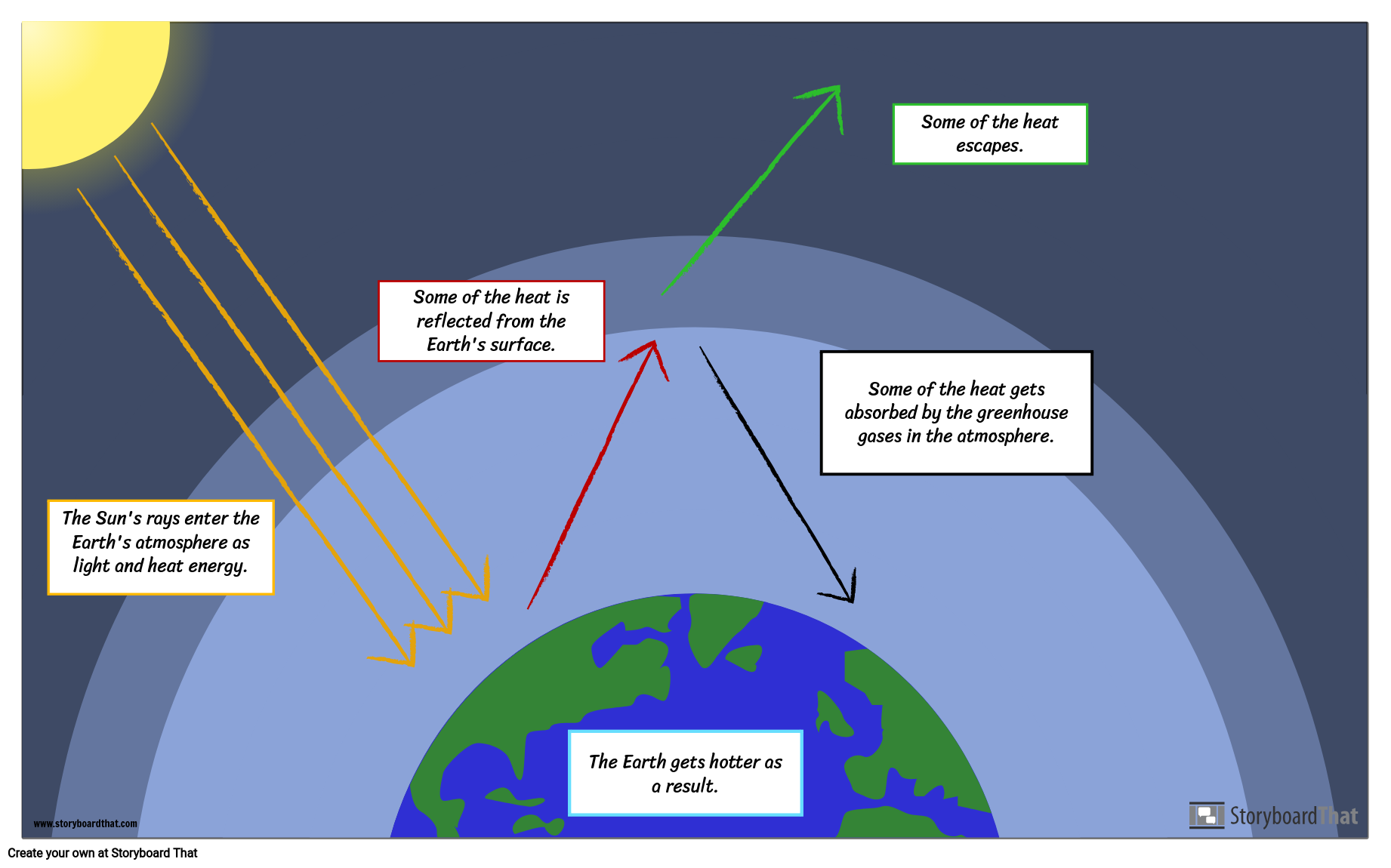



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
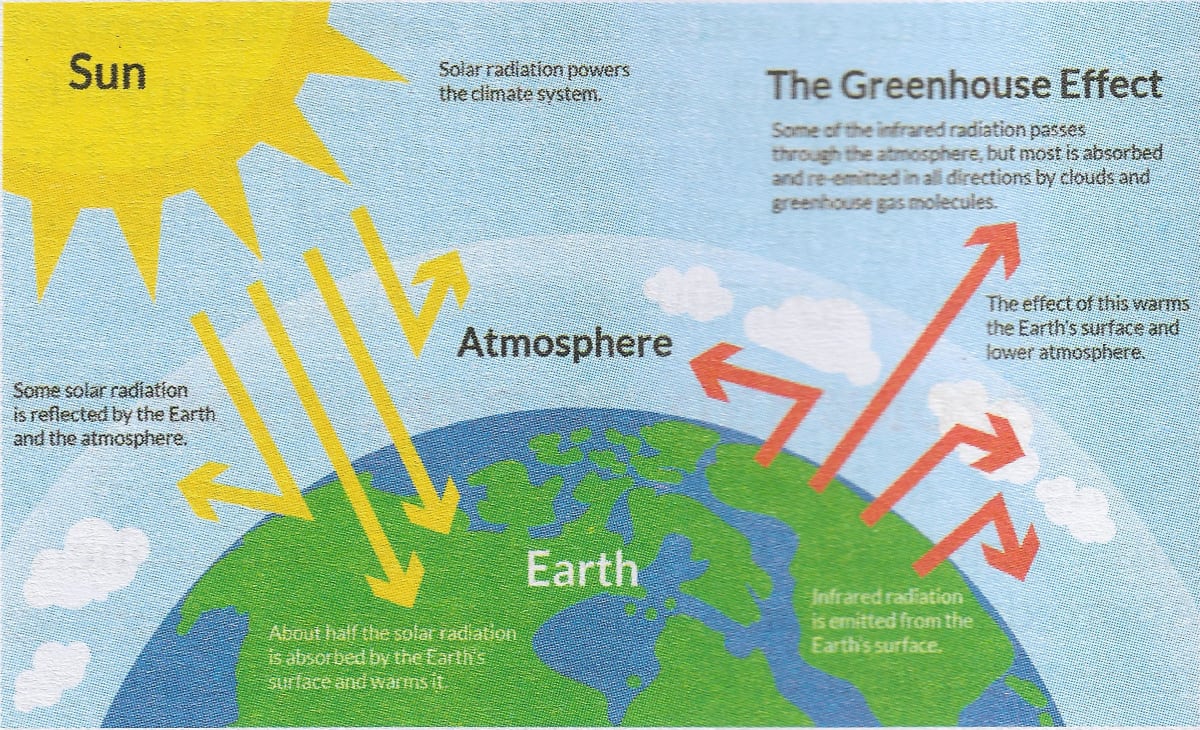
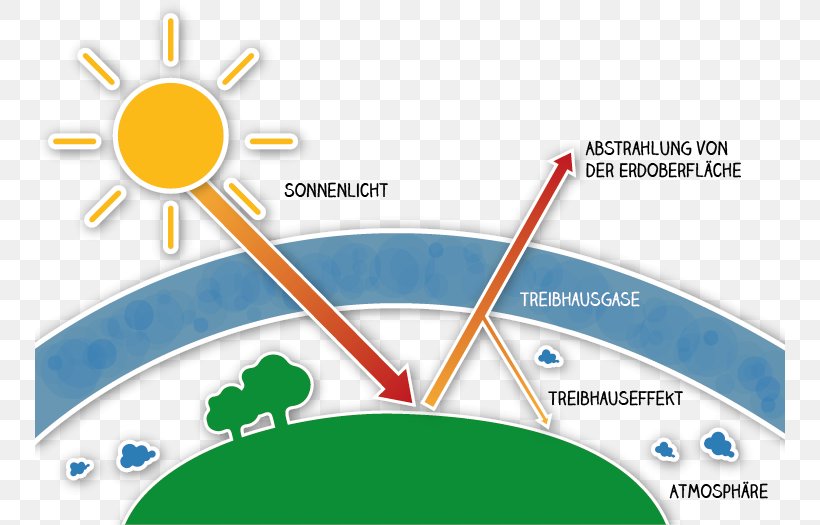
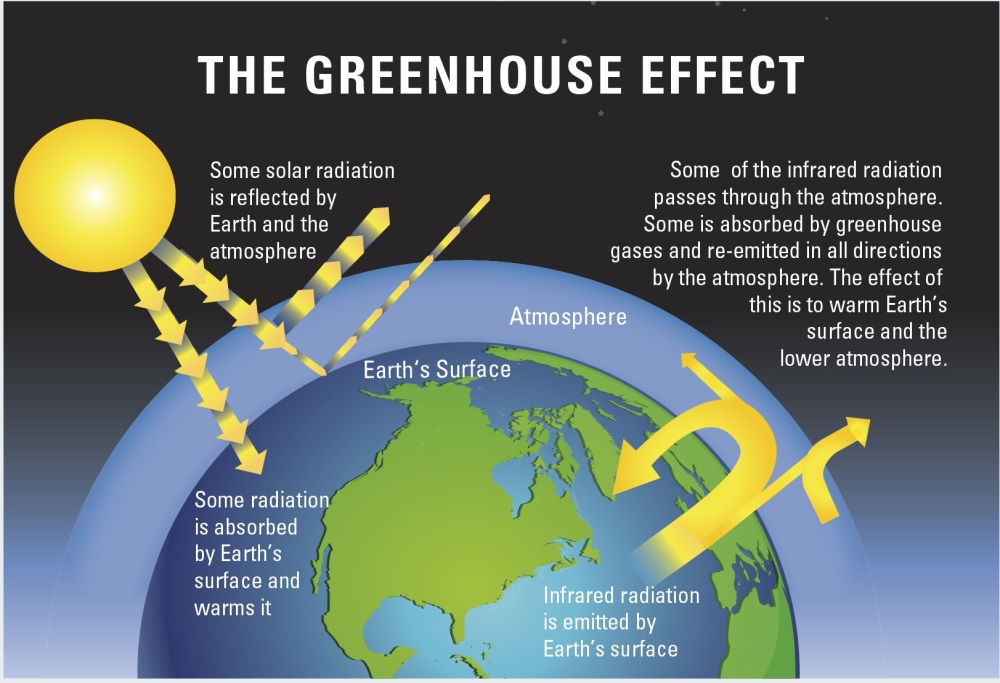
The Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planetWhat – specifically – does the term "global warming" refer to? Build a simple model to recreate the greenhouse effect Record observations of global warming during experiments Compare their model environment with their environment Describe how global warming may impact an engineer's decisions, their own lives and the Earth Discuss their roles as citizens in the reduction of greenhouse gases
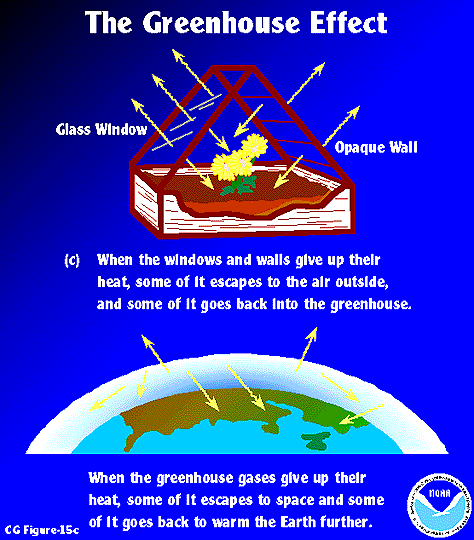



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
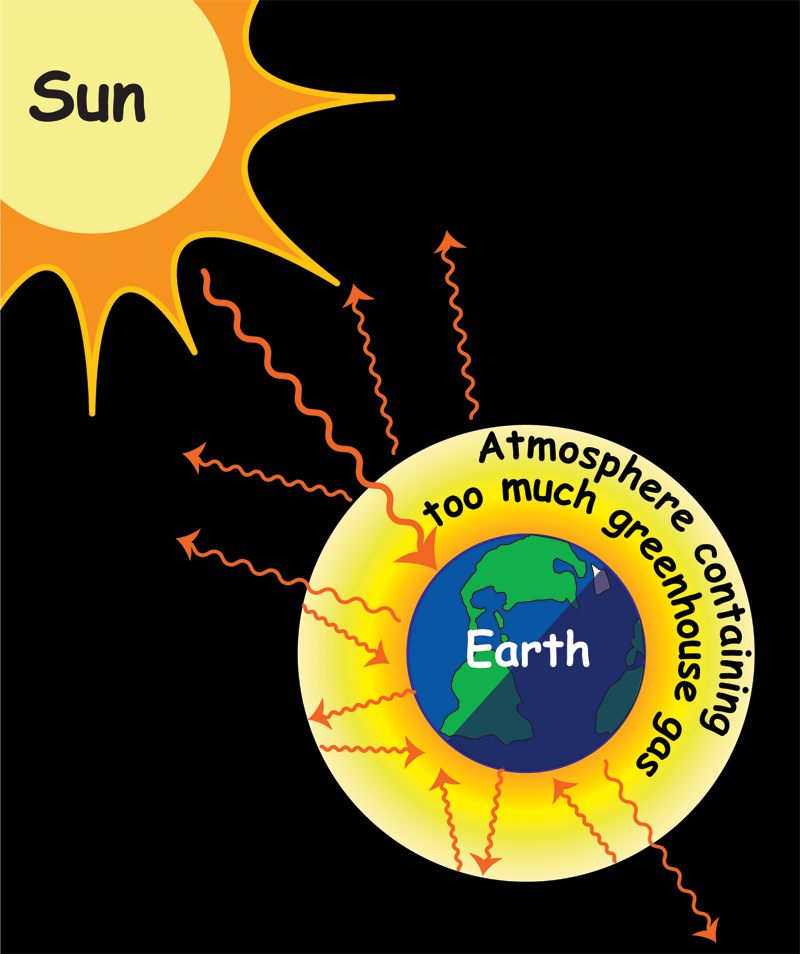



Earth Cartoon Drawing Clipart Earth Diagram Drawing Transparent Clip Art
Explain Complete the following chart regarding the natural and anthropogenic sources of greenhouse gasesThe greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itComparisons Both processes contribute to Earth's temperature/global warming Same amount of heat energy is produced by the sun & reaches the atmosphere Sun's production of energy is a major role in greenhouse and enhanced greenhouse effect CO2 plays a major role in existence of both processes CO2 & other gases block transmission of long wavelength radiation




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube
Additional warming is commonly referred to as Greenhouse Warming Greenhouse Warming is global warming due to increases in atmospheric greenhouse gases (eg, carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, etc), whereas Global Warming refers only to the observation that the Earth is warming, without anyExplain how the greenhouse effect works (you may draw a diagram) Do all greenhouse gases have the same warming effect on the Earth system?The greenhouse effect is a natural process that maintains the temperature of the earth But when the number of greenhouse gases increases in the atmosphere, it results in a phenomenon known as global warming, which is one of the major problems that the world is facing today




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentAbout % is absorbed in the atmosphere (primarily by water vapor, clouds, 4Global Warming A Science Overview TheFigure 2 provides a schematic diagram of the energy fluxes that determine the Earth's temperature (and climate) Of the solar radiation reaching the top of the atmosphere, about 30% is reflected back to space by the atmosphere (primarily by clouds) and the surface;




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Explain how the greenhouse effect works (you may draw a diagram) Do all greenhouse gases have the same warming effect on the Earth system? Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) cooler ,002 greenhouse effect stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect stock video clips of 1 greenhouse effect diagram commercial spraying water on plants greenhouse gas effect global warming posters sun earth diagram energy poster global warming global warming solutions sun radiating to a plant
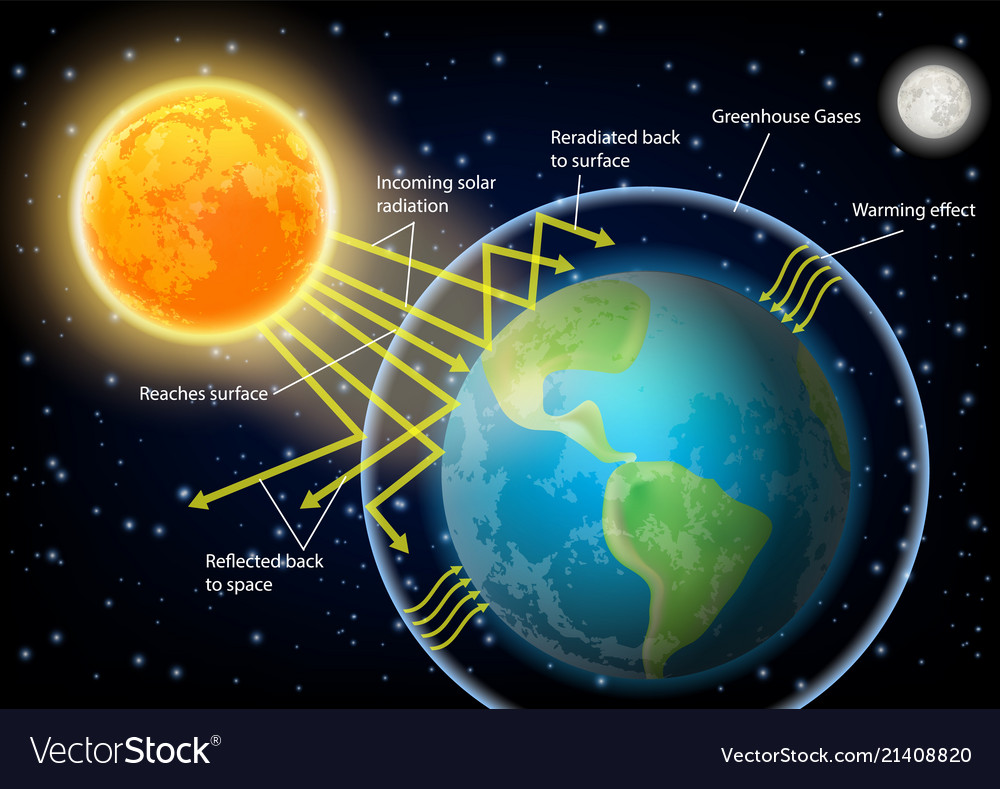



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear French mathematician Joseph Fourier isBy Shelly Coe and Sara Halma Objective To make students aware of the theory of global warming, greenhouse effect, the changes that occur because of the above and finally, the adaptations that may need to be used Time The actual unit is set up for 5 class periods Special note There is a lab that must be started 3 weeks prior to the unitActivity 11 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 7 – 9 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will do a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect, and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 The Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion




Global Warming Group Activity




5 2 1 Draw And Label A Diagram
Explain Complete the following chart regarding the natural and anthropogenic sources of greenhouse gasesGlobal warming is the increase in the average measured temperature of the Earth's nearsurface air and oceans since the midth century, and its projected continuation In media, it is synomonous with the term "climate change Global surface temperature increased 074 ± 018 °C during the 100 years ending in 05The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)Global Warming is the increase in global temperatures due to the increased rate of the Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases trap the incoming solar radiation, these gases include Carbon Dioxide, CFCs, Methane, Nitrous Oxides and other Halocarbons These are released by human activity We need the Greenhouse effect to maintain life on earth as we know




Easy Greenhouse Effect Drawings




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
Surrounding the greenhouse effect and global warming Here's how you can help Task 1 Draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect Label it carefully Task 2 Below your diagram write a concise paragraph that explains the diagram Write neatly and use correct English!Greenhouse effect and Global Warming A greenhouse is a structure whose roof and walls are made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown In a greenhouse, the incident solar radiation




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Name Global Climate Change Webquest Greenhouse Effect Go To



Simple




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




Heat Transfer In The Atmosphere Physical Geography




Global Greenhouse Gases Emission And Their Characteristics Greenhouse Effect The Largest Emitting Countries Carbon Dioxide Canstock



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Global Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That Is A Great Way For Students To Combine Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Ciencias Naturales Dieta Balanceada Ciencia




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
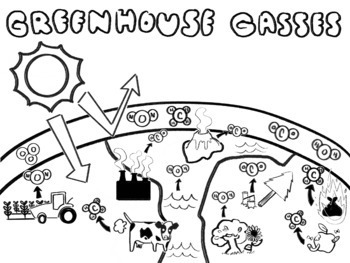



Greenhouse Gases Coloring Page Natural Vs Anthropogenic Bundle Tpt




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
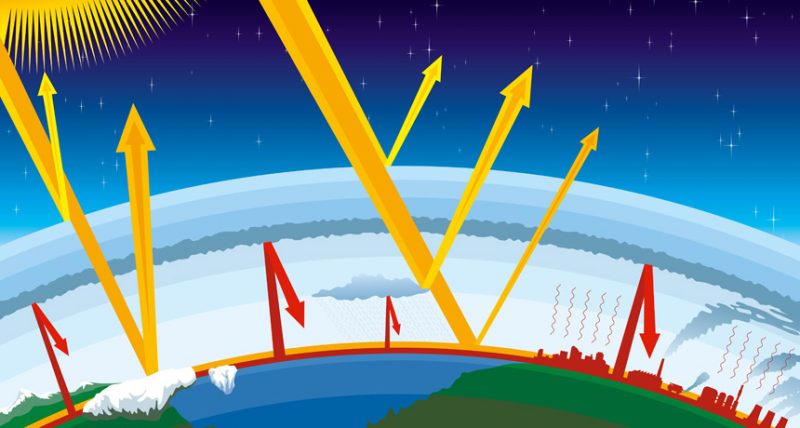




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
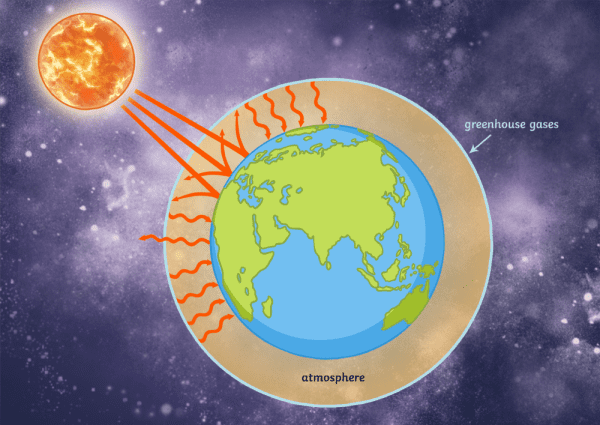



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram
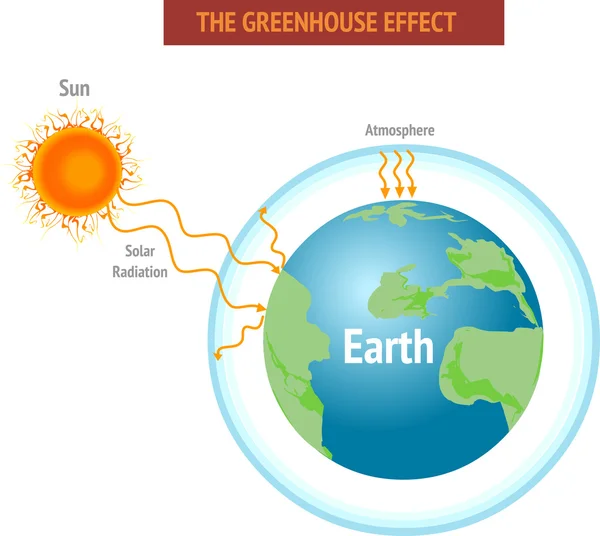



1 659 Greenhouse Effect Vector Images Greenhouse Effect Illustrations Depositphotos



Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Png Clipart Brand Circle Diagram Drawing Encapsulated Postscript Free Png Download




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Works Global Warming Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Easy Greenhouse Effect Drawings



Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




1 659 Greenhouse Effect Vector Images Greenhouse Effect Illustrations Depositphotos



The Greenhouse Effect



1




Greenhouse Effect Illustrations And Clipart 2 368 Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Illustrations And Drawings Available To Search From Thousands Of Stock Vector Eps Clip Art Graphic Designers




I With The Help Of A Neat Labelled Diagram Depcit The Cycling Of Carbon In Nature Ii Mention Two Ways In Which Carbon Dioxide Is Fixed In The Environment Or I Describe




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Emission




Global Warming Diagram Global Warming Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Effect



Global Warming




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Illustration Stock Vector Image Art Alamy




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change
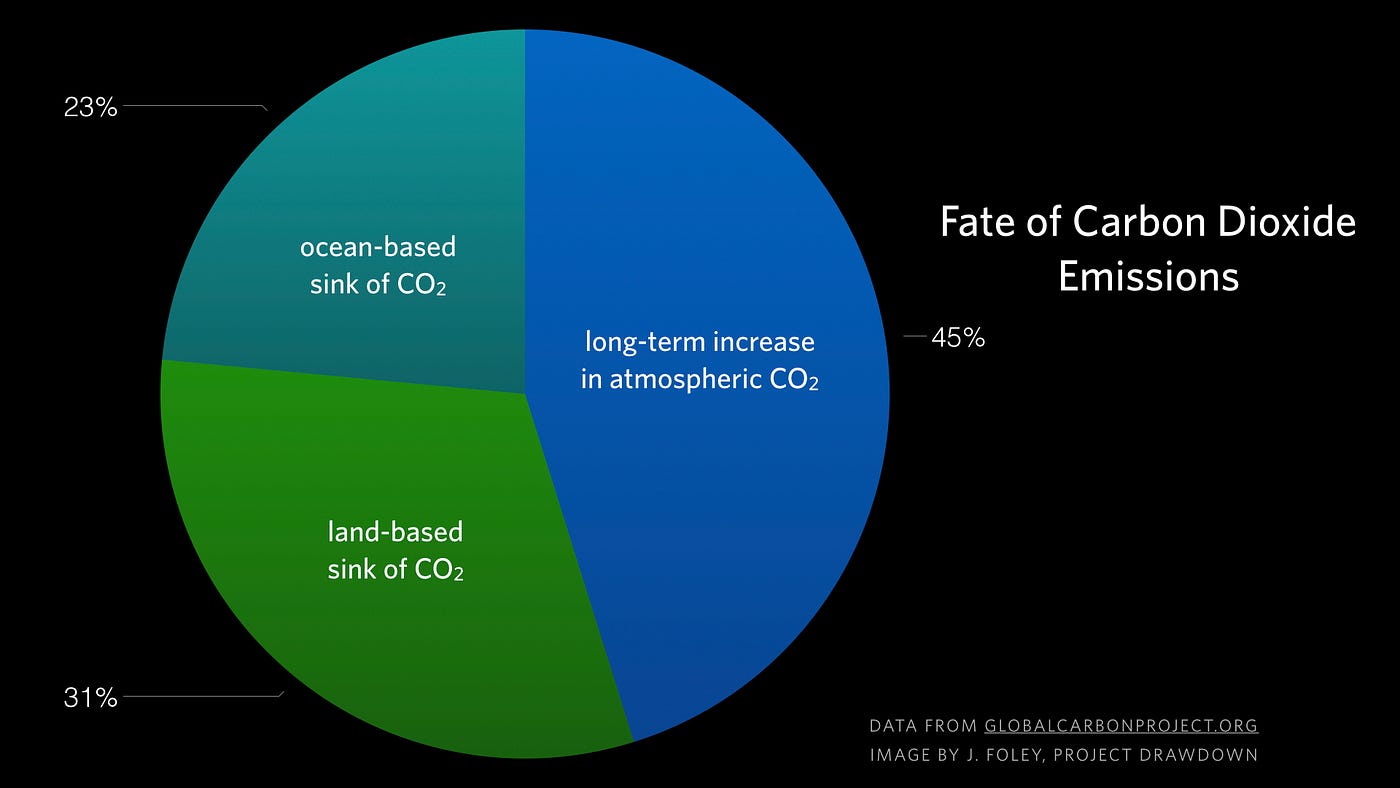



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Worksheets Greenhouse Effect Diagram Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Lesson Global Warming Project




Draw A Well Labelled Diagram To Explain The Greenhouse Knowledgeboat
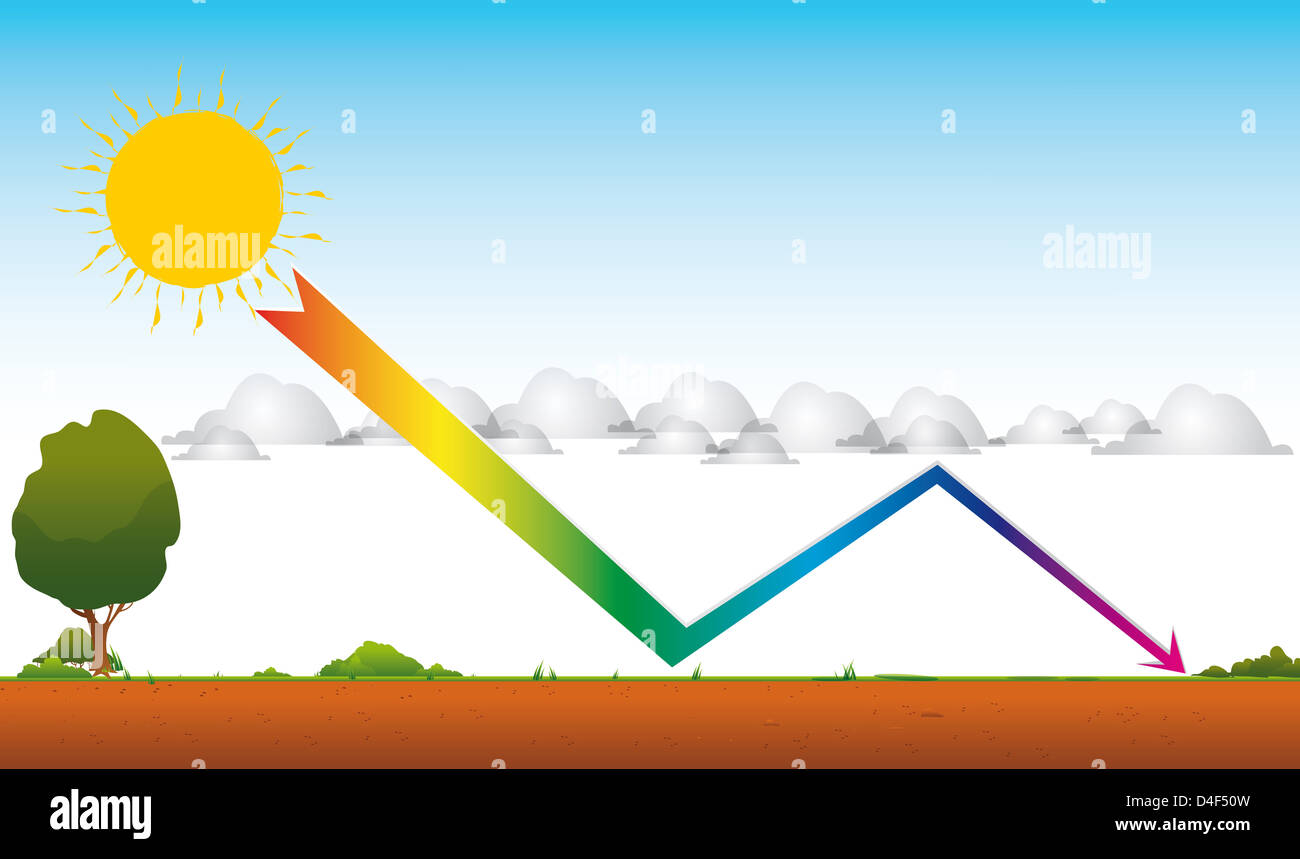




Drawing Of Global Warming By A Greenhouse Effect An Arrow From The Sun Through The Clouds Toward The Ground Stock Photo Alamy
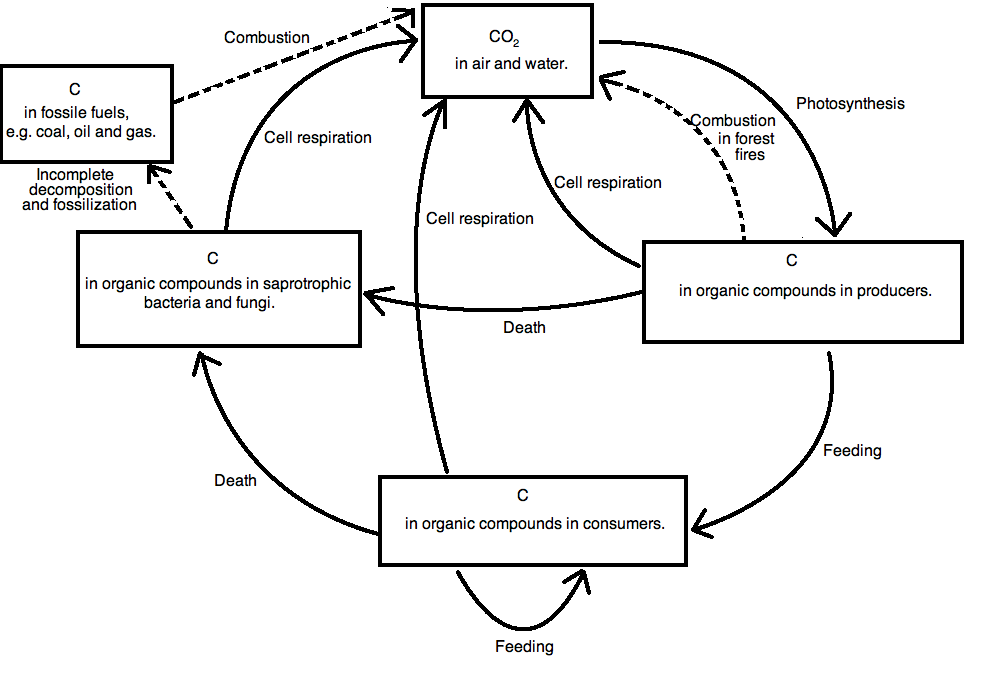



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



How Deforestation Contributes To The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
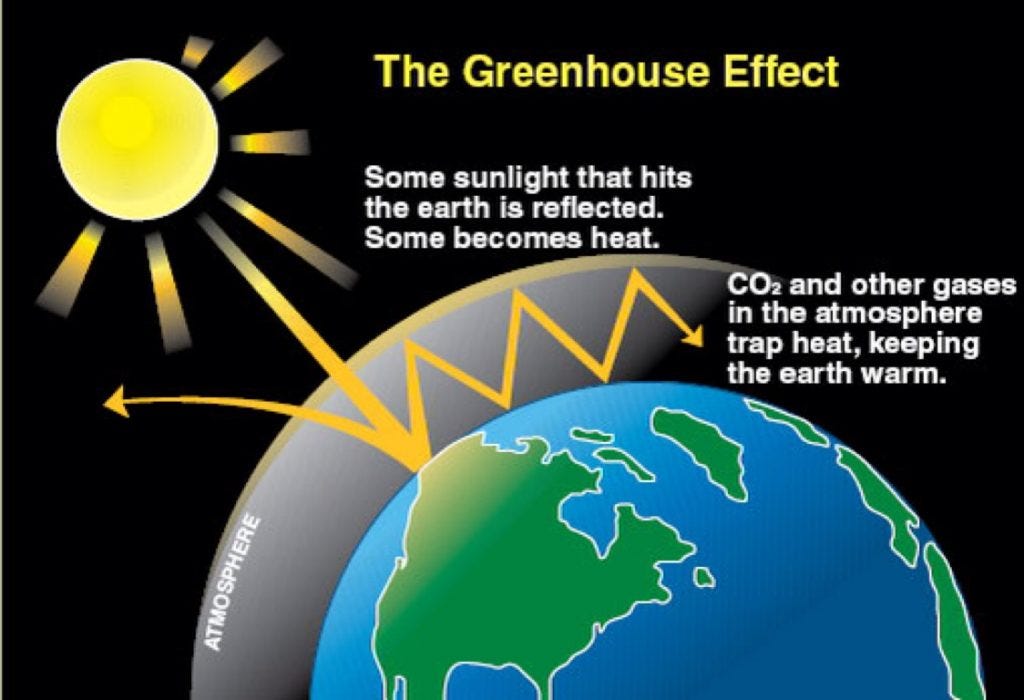



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium



Climate Change Icon Earth Globe Suffering Global Warming Simple Vector Illustration Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
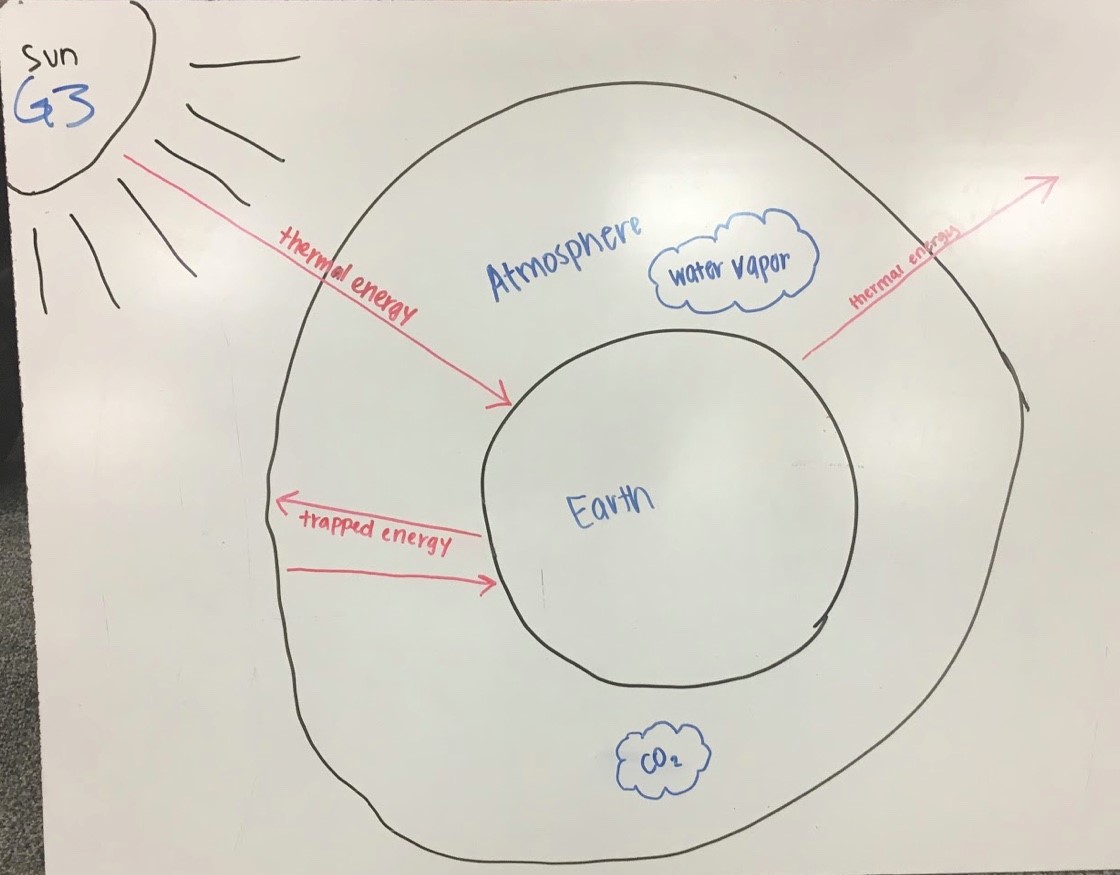



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic
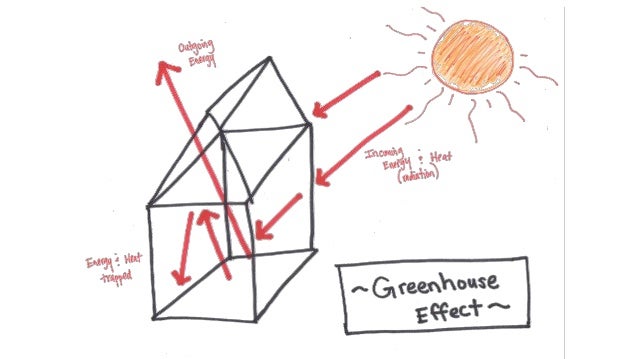



Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Natural And Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing Solar Radiation And Planet Earth Global Warming Climate Change Canstock



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



3
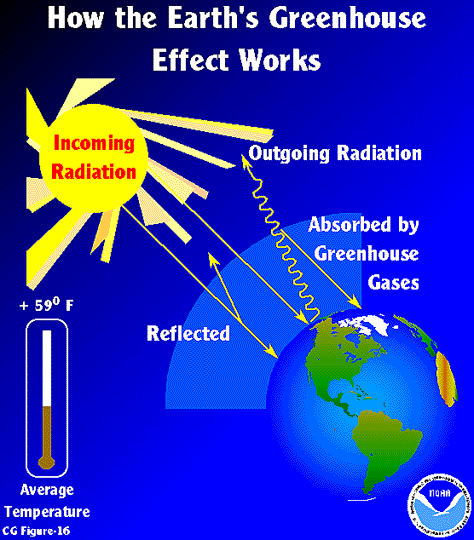



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
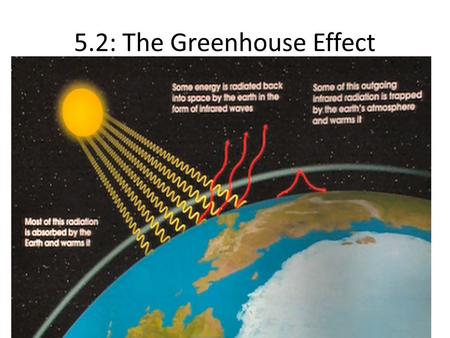



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




How Should Climate Change Be Taught In Schools Across America Ensia




Greenhouse Effect Word Cloud Greenhouse Effect Word Cloud On A White Background Canstock




Example Of Student Drawing Based On Textbook Diagram Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Greenhouse Effect




Easy Greenhouse Effect Drawings




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube
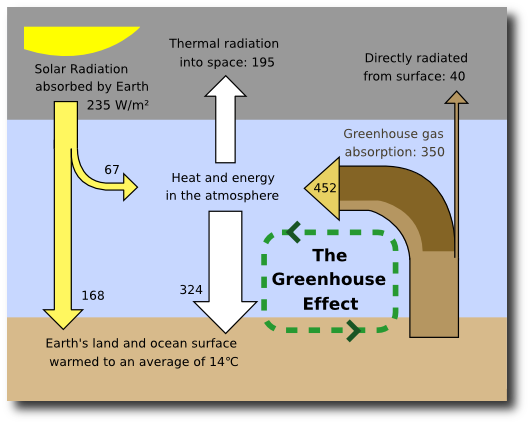



Climate Change And Global Warming Introduction Global Issues




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
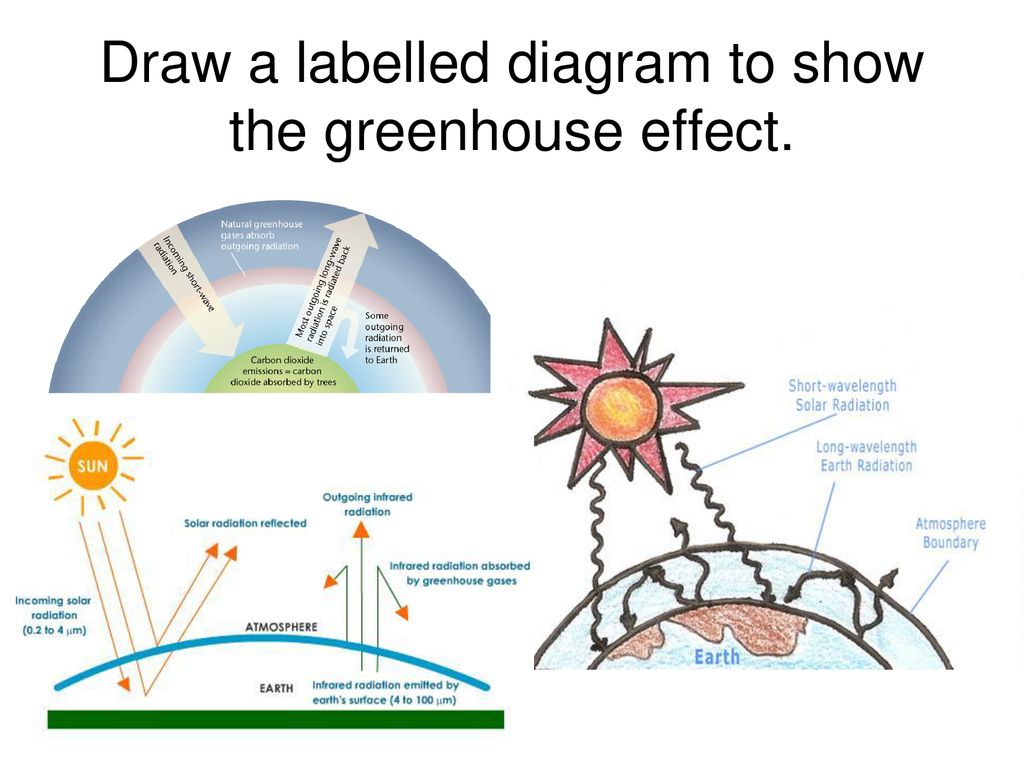



Lesson Ppt Download




Cyberphysics Global Warming



Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿