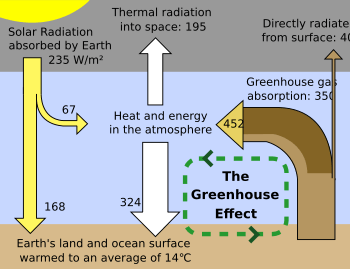
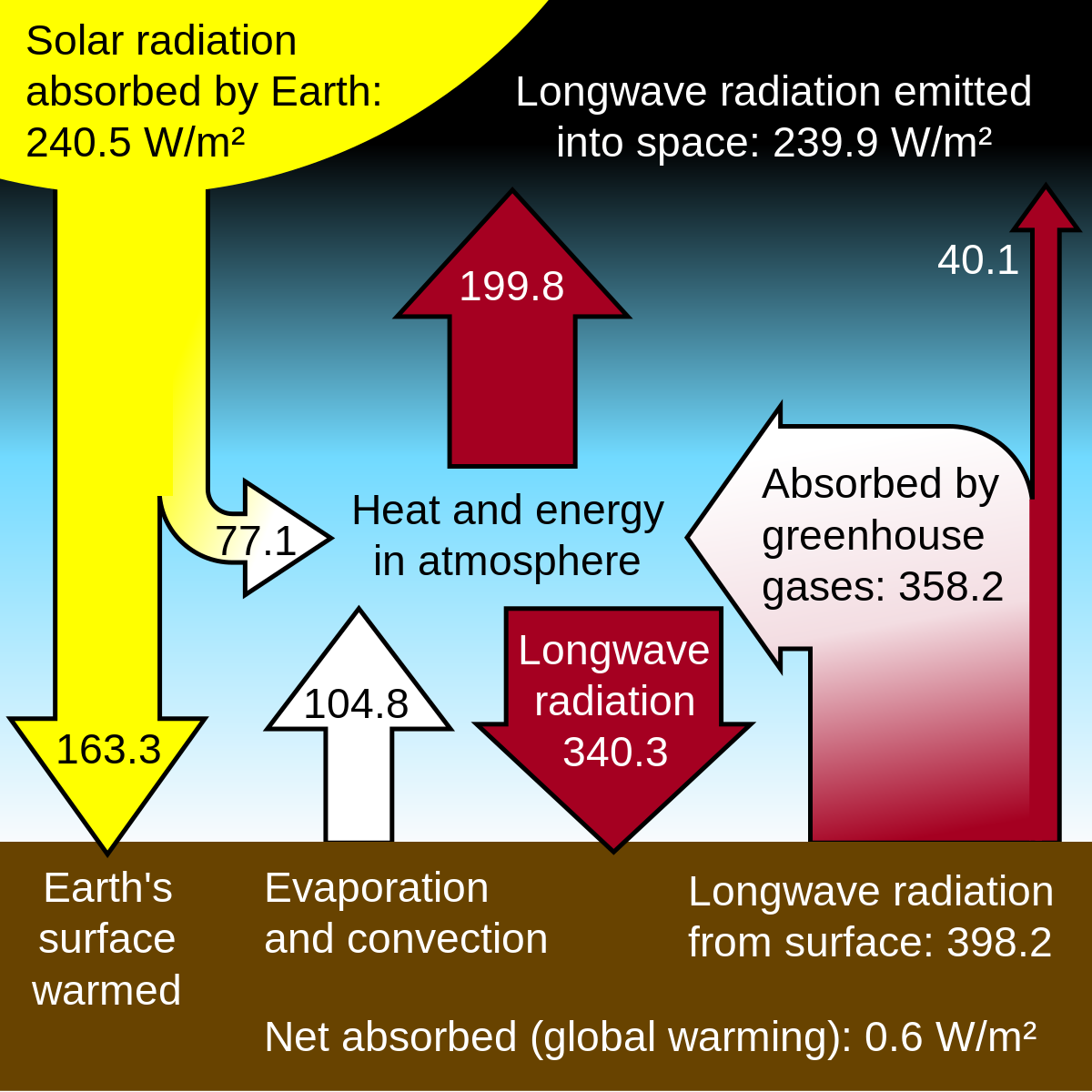
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the makeup of our atmosphere Earth is sometimes called the "Goldilocks" planet – it's not too hot, not too cold, and Finally, What is the greenhouse gas quizlet?, What are green house gases?
Mass Extinctions And Climate Change Why The Speed Of Rising Greenhouse Gases Matters
Greenhouse gases definition quizlet
Greenhouse gases definition quizlet-The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement adopted in 1997 that aimed to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and the presence of greenhouse gases Definition Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effect




Mass Extinctions And Climate Change Why The Speed Of Rising Greenhouse Gases Matters
The greenhouse effect is caused by gases in our atmosphere trapping in heat to keep the planet warm The enhanced greenhouse effect is caused by a rise in greenhouse gas emissions leading to more heat being trapped, which results in a warmer planet Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide and methane Carbon dioxide is produced from the burning of fossil fuels like coal and gasA carbon footprint is figured out by the amount of these greenhouse gases that are released into the environment either directly or indirectly by our actions (usually in bunches annually) This can be used to people, families, agencies, events, items as well as also countries Why It Is Necessary To Know Your Carbon Footprint Examples of these gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone How do greenhouse gases affect Earth's atmosphere quizlet?
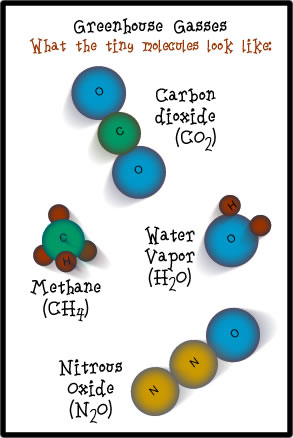
Greenhouse gases are certain molecules in the air that have the ability to trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere Some greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and methane (CH 4 ), occur naturally and play an important role in Earth's climateFluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6Any gases compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere
Gases (water vapour and co2greenhouse gases) trap the heat 1temp on earth is risen by 8 % 2 more and more greenhouse g What determines climate on earth Negotiators are meeting in the lead up to the United Nations' 21st Conference of the Parties in December this year In Paris, the hope is that the world's governments will come to an agreement on how much and how quickly countries will limit their emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, in order to ensure that the world's climate does not warm by moreSelect one a Uncertain historic levels of greenhouses gases because records are unclear b Uncertain connections between greenhouse gases and climate c Uncertainties about new sources of greenhouse gases d Interactions between components of the climate system that can either magnify or constrain climate change




Cause And Effect Definition Quizlet




Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeThe clear effect of the greenhouse gases is the stable heating of Earth's atmosphere and surface, thus, global warming The abi lity of certain gases, greenhouse gases, to be transparent toGreenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth's average temperature would be about 60º F colder



Greenhouse Gas Facts For Kids




Hot Topic Greenhouse Effect Abijoyswanson
Voluntary Reporting of Greenhouse Gases, US Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration (16 pp, 111K, About PDF) Acres of US forests sequestering CO 2 for one year Forests are defined herein as managed forests that have been classified as forests for over years (ie, excluding forests converted to/from other landuse types)Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without themThe reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphereWhen energy from theThe greenhouse effect occurs when sunlight strikes the Earth These gases help regulate the temperature of Earth Due to the burning of large amounts of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Isb 1 Unit 4 Diagram Quizlet
What do they mean by feedbacks?Greenhouse Gases ___ ___ increase global warming by being transparent to visible light from the sun but translucent to infrared light emitted by the Earth as it tries to cool Transparent As greenhouse gases provide their famous warming effect to Earth's surface, aerosol pollution in the atmosphere actually partly counteracts it Aerosols are tiny particles suspended in the air, both natural and industrial, including seasalt, mineral dust, ash, soot, sulphates, nitrates, and black carbon




3rd Period Environmental Vocab Flashcards Quizlet




Mastery Astronomy Assign 5 Chapter 7 Flashcards Quizlet
Climate change Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases are gas molecules that have the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
The targets apply to the four greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), sulphur hexafluoride (SF 6), and two groups of gases, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and perfluorocarbons (PFCs) The six GHG are translated into CO 2 equivalents in determining reductions in emissionsGreenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vaporВ ВThe Runaway Greenhouse Effect is when a planet's atmosphere has such a high % of greenhouse gases within it that the Sun's incoming radiation cannot escape An illustrative example is If X is a greenhouse Such amplification of the initial CO2 forcing could conceivably lead to a runaway greenhouse effect where the




Chapter 3 Chemistry Of Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
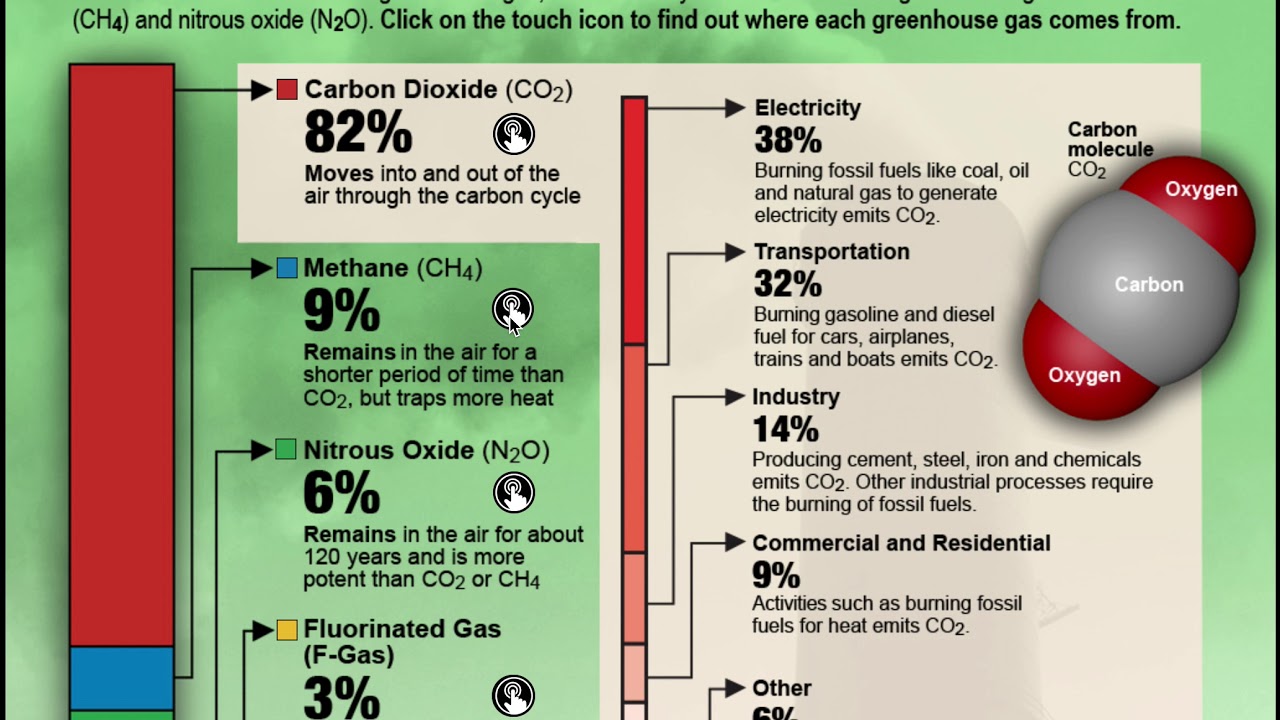
Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerantsGreenhouse Gas Defined The earth's atmosphere is made up of many different types of gases, each of which contributes to the greenhouse effect differently Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and night




Global Climate Change The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Diagram Quizlet




Cdn Zmescience Com Wp Content Uploads 18 05 Greenhouse Effect 960 7 1 Png
Greenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surfaceThe greenhouse effect is primarily a function of the atmospheric concentration of water vapor and carbon dioxide (CO2) and other trace gases such as methane (CH4) and nitrous oxides (N2O) These greenhouse gases occur naturally and play a major role in determining the Earth's temperature by trapping and reflecting heat energy, a process knownMain Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




Greenhouse Effect Esa2 Flashcards Quizlet
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not a




Ib Bio Core 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet



Causes And Greenhouse Effect




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet




Cause And Effect Definition Quizlet



Greenhouse Effect




Climate Change Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




The Greenhouse Gas Effect Diagram Quizlet




What Are Greenhouse Gases Main Sources And Climate Impact




Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Ck 12 Foundation




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



What Are Greenhouse Gases Let S Talk Science
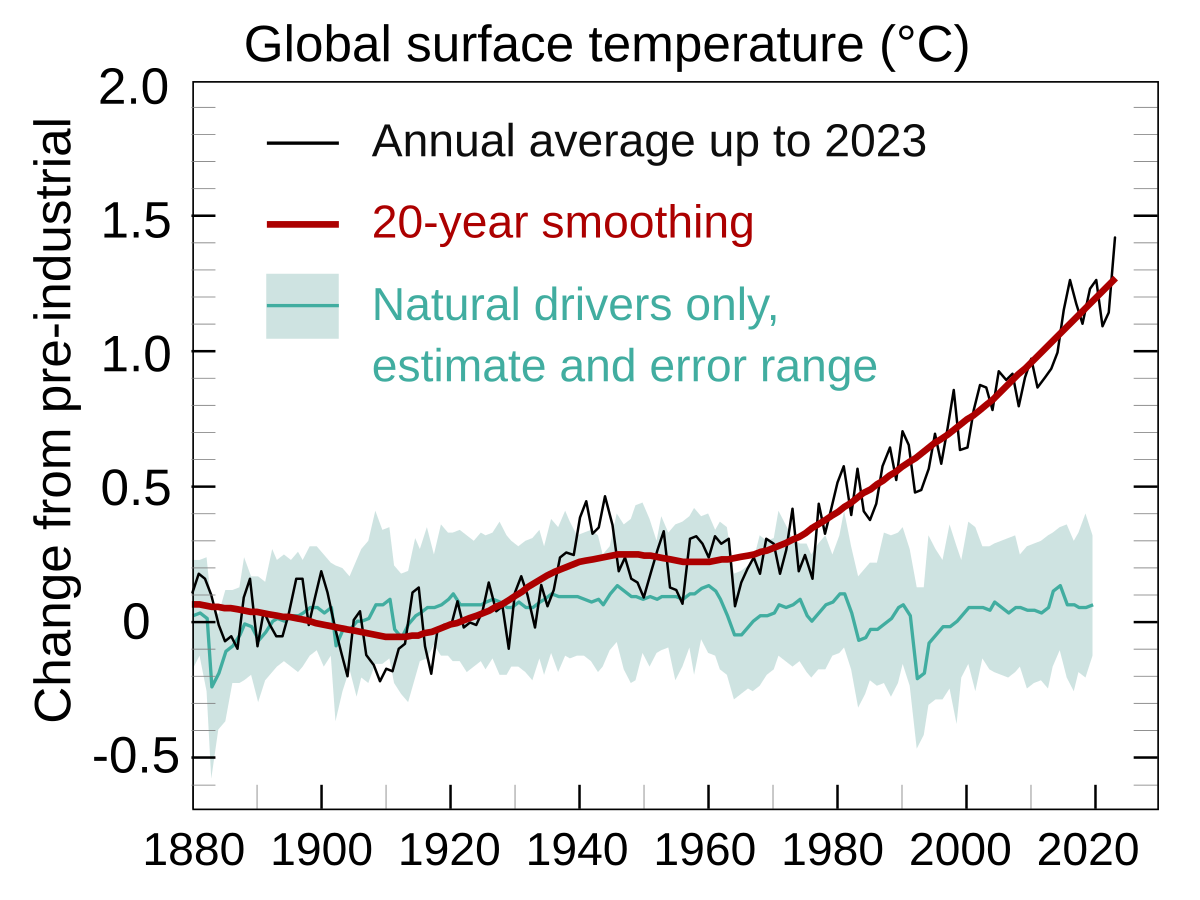



Attribution Of Recent Climate Change Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect Definition Apes




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education



The Greenhouse Effect



Search Q Carbon Dioxide Tbm Isch




Greenhouse Effect Esa2 Flashcards Quizlet




Ib Bio Core 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Ib Bio Core 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
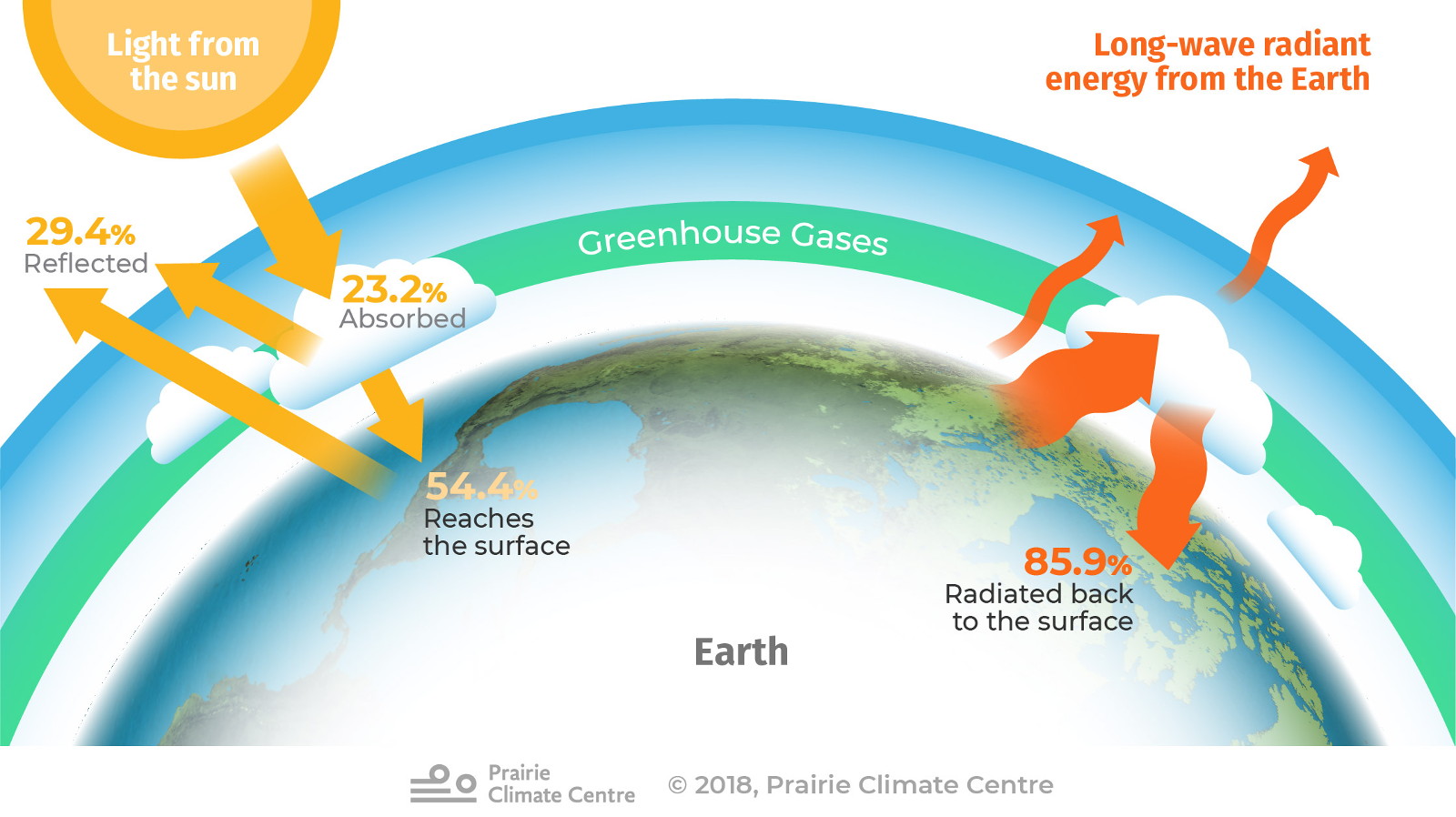



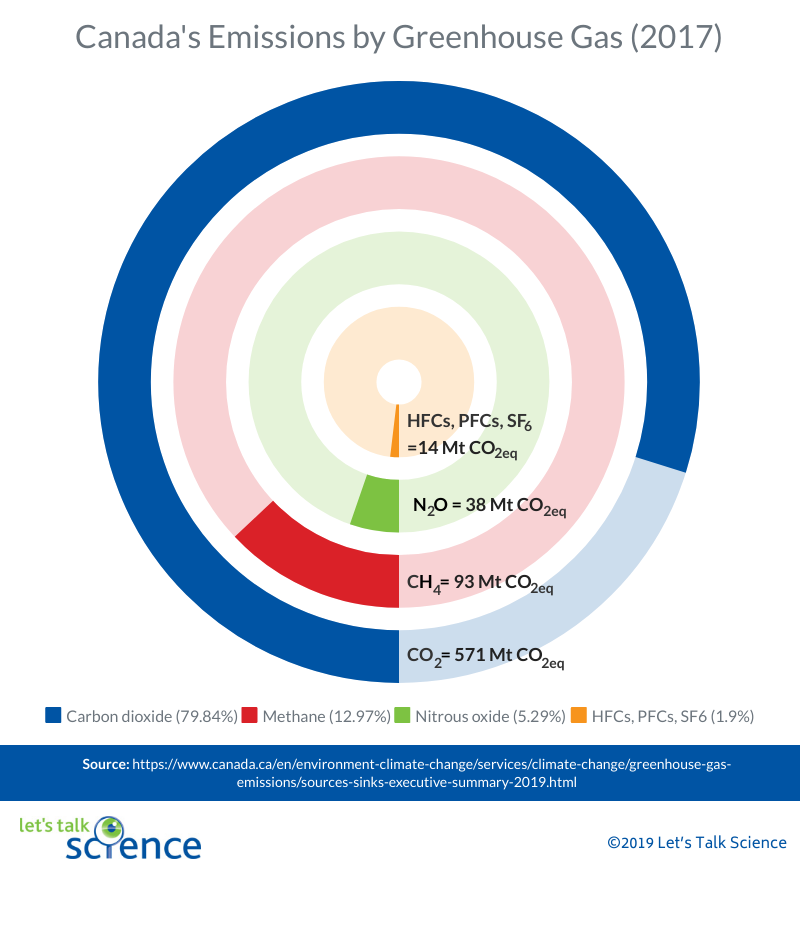
Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada




The Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet



3




Science Quizlet On Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Earth Processes And Risks Quiz V Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Gases Good Or Bad National Geographic Society



Misunderstood Meteorology And Pollution Topics




11 The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
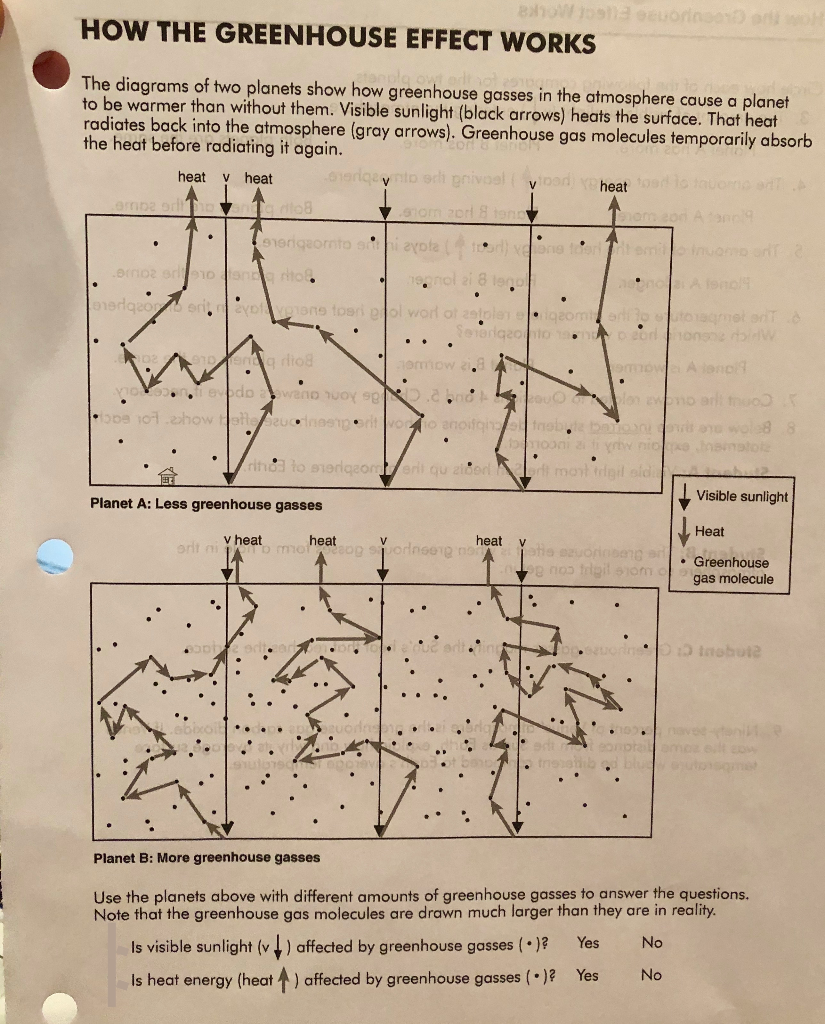



How The Greenhouse Effect Works The Diagrams Of Two Chegg Com




Greenhouse Gases Overview Beef2live Eat Beef Live Better




Climate Change Diagram Quizlet




Earth S Energy Balance Diagram Quizlet
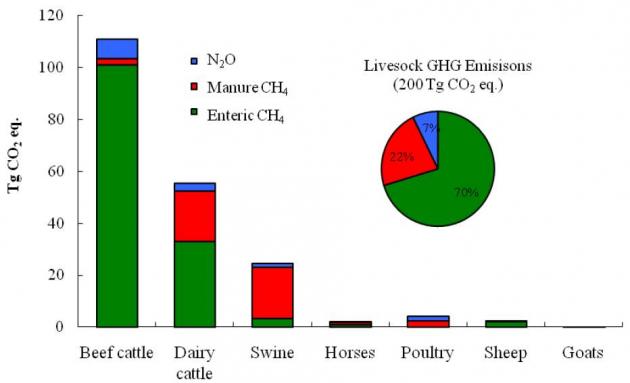



Sources Of Agricultural Greenhouse Gases Livestock And Poultry Environmental Learning Community




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension




Apes Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Ozone Layer Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet



Greenhouse Gases




Changing Climate Flashcards Quizlet




10 Flashcards Quizlet




The Greenhouse Effect Introduction To Chemistry




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Human Impacts On The Environment Mr L Diagram Quizlet




Chapter 19 Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Cc17c The Atmosphere Today Diagram Quizlet




Apes Ch 12 13 Flashcards Quizlet




Mass Extinctions And Climate Change Why The Speed Of Rising Greenhouse Gases Matters




The Greenhouse Effect Mechanism




Chapter Flashcards Quizlet




Ib Geography Global Climate Vulnerability And Resilience Flashcards Quizlet




Hot Topic Greenhouse Effect Abijoyswanson



Climate Change And Greenhouse Gases Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter 3 Chemistry Of Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect And Climate Change Flashcards Quizlet




Global Warming And Climate Change Biodiversity And Succession Vocab Flashcards Quizlet




Do Now 9 24 Write The Definition Of The Green House Effect In Your Notes Greenhouse Effect Gases In The Lower Troposphere That Cause The Greenhouse Ppt Download




Bio Chapter Homework Flashcards Quizlet
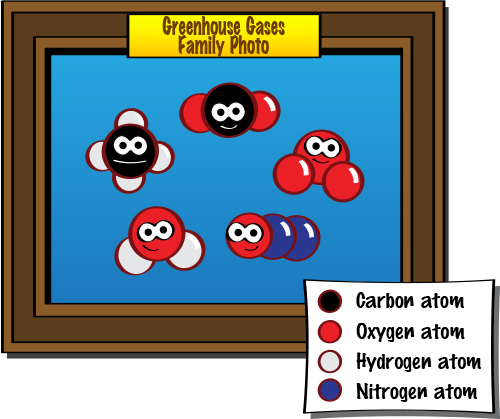



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Properties Of Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect
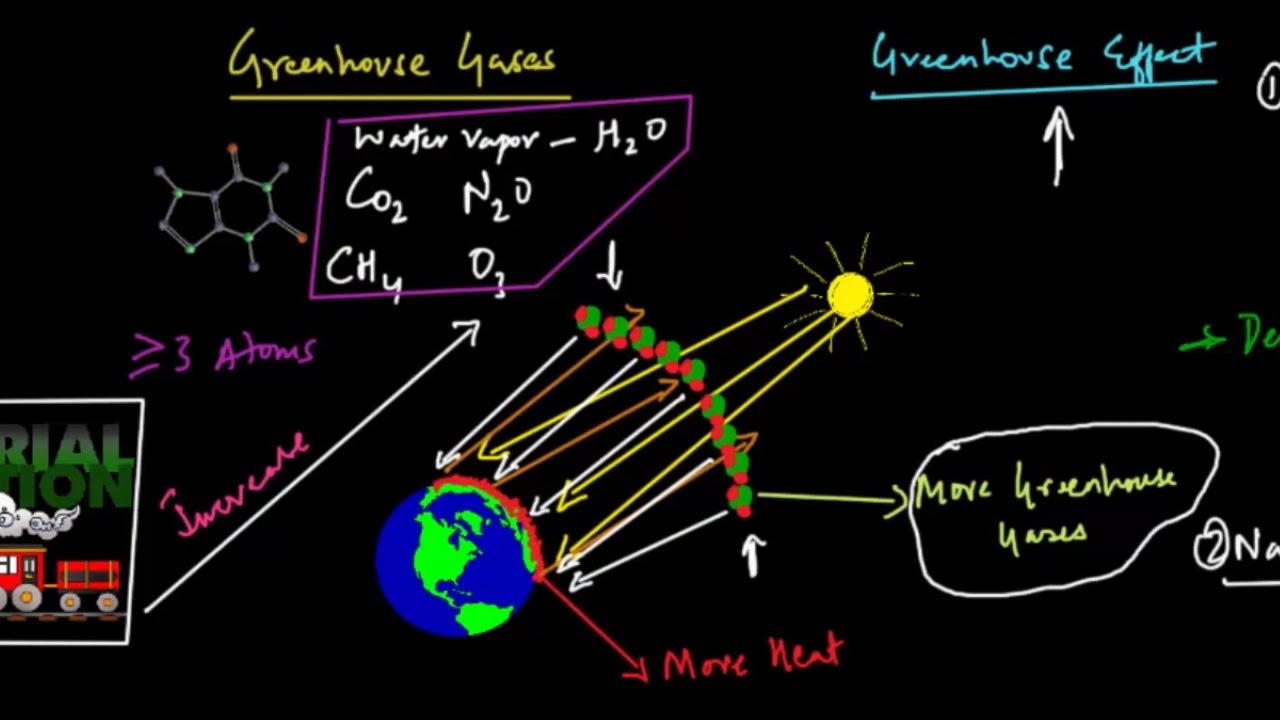



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube




What Is The Greenhouse Effect S3 Geography Maldives Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Geography Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau




Unit 3 Climate Change Practice Problems Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Noxious Gases Agriculture Diagram Quizlet




The Green House Effect Flashcards Quizlet




Human Causes Of Climate Change National 5 Geography Climate Change Diagram Quizlet



Greenhouse Gases
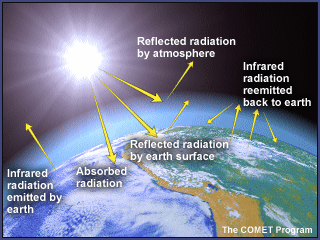



The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




13 5 Atmospheric Pollutants Diagram Quizlet




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica
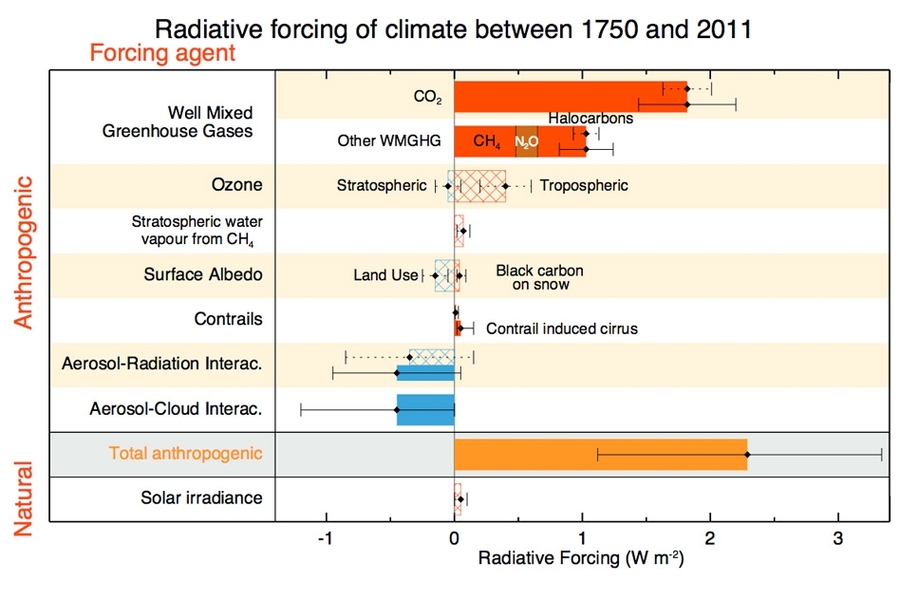



Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Earth Systems Diagram Quizlet




3rd Period Environmental Vocab Flashcards Quizlet




Noaa Global Monitoring Laboratory The Noaa Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Aggi




9 1 The Earths Atmosphere Flashcards Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect 1 Flashcards Quizlet



1
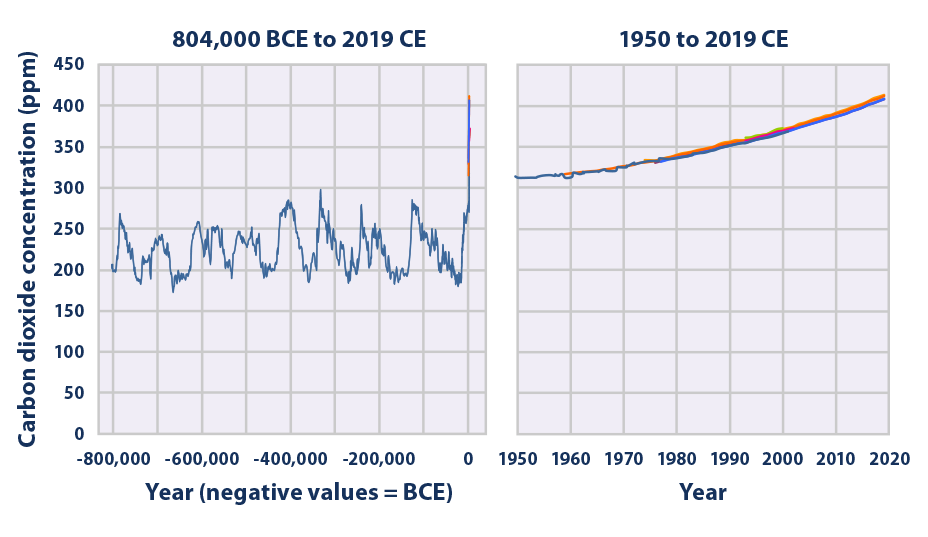



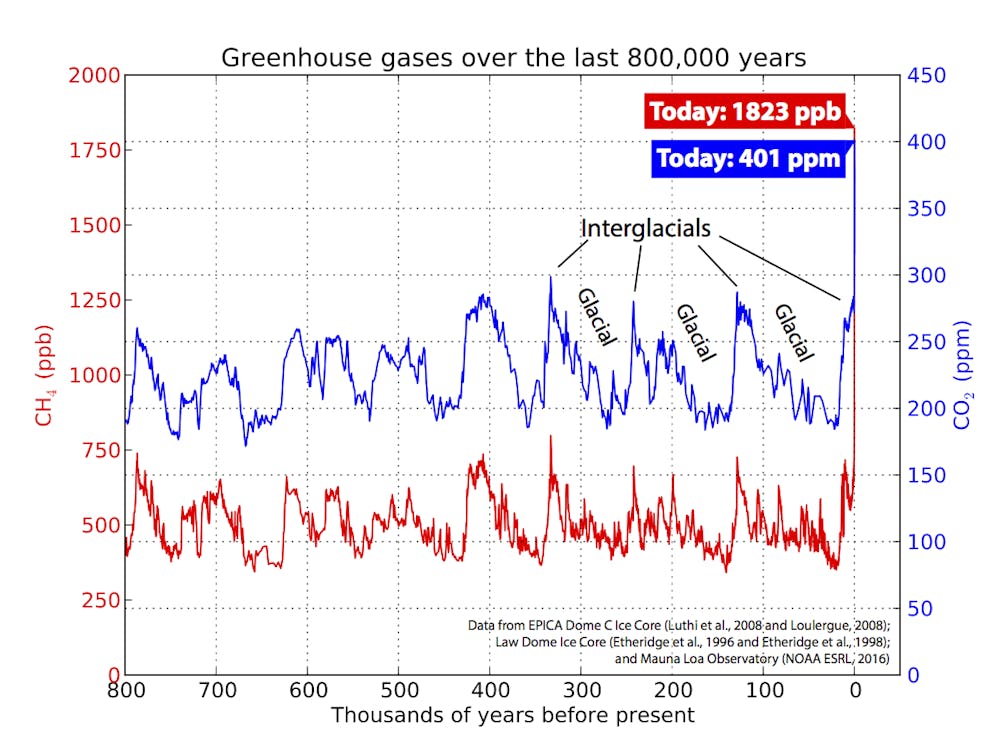
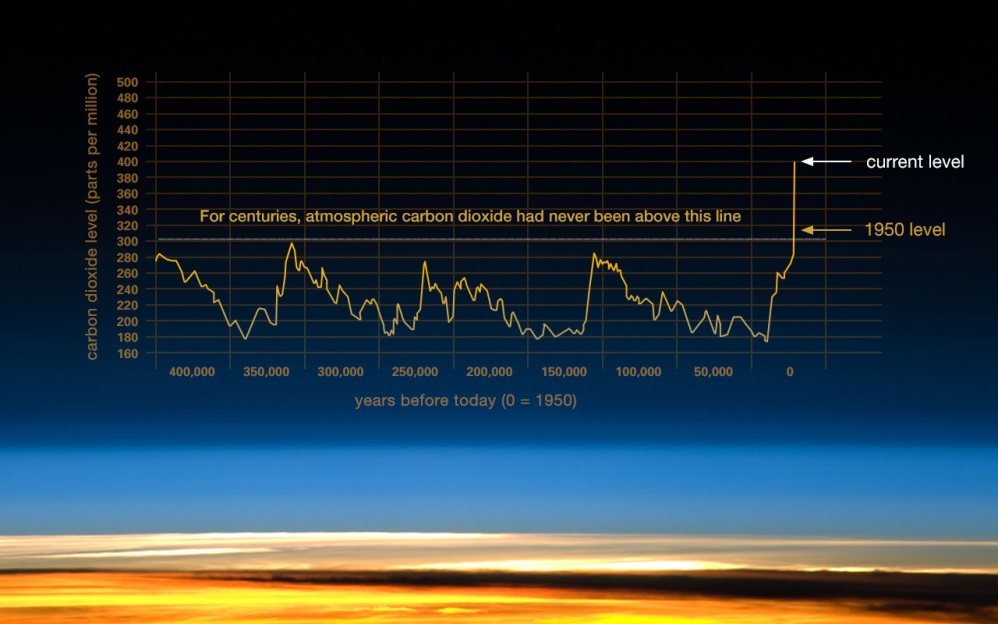
Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿